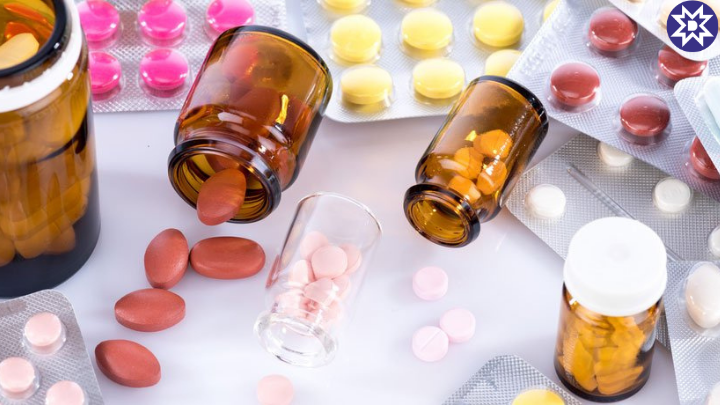
Pharmaceutical packaging plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety, effectiveness, and integrity of medicines. It is not only about convenience but also about protecting the contents from contamination, damage, and tampering.
1. Functions of Pharmaceutical Packaging
Pharmaceutical packaging serves multiple purposes:
- Protection: Shields medicines from environmental factors such as light, moisture, oxygen, and temperature fluctuations, which can degrade their quality.
- Information: Provides essential details like dosage instructions, expiration dates, batch numbers, and warnings.
- Identification: Helps patients and healthcare providers recognize medicines correctly to avoid errors.
- Tamper Evidence: Ensures that the product has not been opened or altered before reaching the consumer.
2. Types of Pharmaceutical Packaging
Common types of pharmaceutical packaging include:
- Primary Packaging: Directly contacts the medicine, such as blister packs, bottles, vials, and tubes.
- Secondary Packaging: Surrounds primary packaging, like cartons and boxes, providing extra protection and space for labeling.
- Tertiary Packaging: Used for bulk handling and shipping, such as pallets and crates, ensuring safe transportation.
Each type is designed to maintain medicine stability and comply with regulatory standards.
3. Materials Used in Pharmaceutical Packaging
Pharmaceutical packaging materials are carefully selected to maintain safety and effectiveness:
- Plastic: Lightweight and versatile; often used for bottles, syringes, and tubes.
- Glass: Chemically inert and ideal for injectables or liquid medicines.
- Aluminum Foil: Common in blister packs, protecting tablets from moisture and light.
- Paperboard and Cartons: Provide secondary protection and space for labeling.
The choice of material depends on the medicine type, shelf-life requirements, and regulatory compliance.
4. Safety Features in Packaging
To prevent misuse or contamination, modern pharmaceutical packaging often includes:
- Child-resistant caps to prevent accidental ingestion
- Tamper-evident seals to indicate if the product has been opened
- Barcodes and QR codes for traceability in the supply chain
- Anti-counterfeit measures such as holograms or unique identifiers
These safety features protect both patients and healthcare providers.
5. Environmental Considerations
Pharmaceutical packaging also considers sustainability:
- Using recyclable plastics and paper
- Minimizing excess packaging to reduce waste
- Developing biodegradable or eco-friendly alternatives
Balancing safety, usability, and environmental impact is a growing priority in pharmaceutical design.
Conclusion
Pharmaceutical packaging is a critical component of healthcare, ensuring medicines remain safe, effective, and easy to use. By understanding the science behind packaging, consumers and professionals can appreciate the importance of proper storage, labeling, and safety features.